DC-DC Converter and Wireless Power Transfer
A DC-to-DC converter is an electronic circuit or electromechanical device that converts a source of direct current (DC) from one voltage level to another. It is a type of electric power converter [1].
In this topic, we are focusing on the optimal design, control system, and new topology. Wireless power transfer is one of the branches of this research topic.
Wireless power transfer (WPT) is the transmission of electrical energy without wires as a physical link [2]. wireless power transfer is widely applied in electric vehicles, wireless sensor networks, liquid crystal displays (LCDs), LED lighting, phone charger, and biomedical applications.
 |
|
Wireless power transfer application |
A wireless power transmission system can be divided into two methods: magnetic induction (or inductive power transfer-IPT) and electrostatic induction (or capacitive power transfer-CPT) [3]. Inductive power transfer uses the magnetic file to transfer the energy and capacitive power transfer uses electric fields instead of magnetic fields to transfer energy.
 |
|
Capacitive wireless power transfer |
 |
|
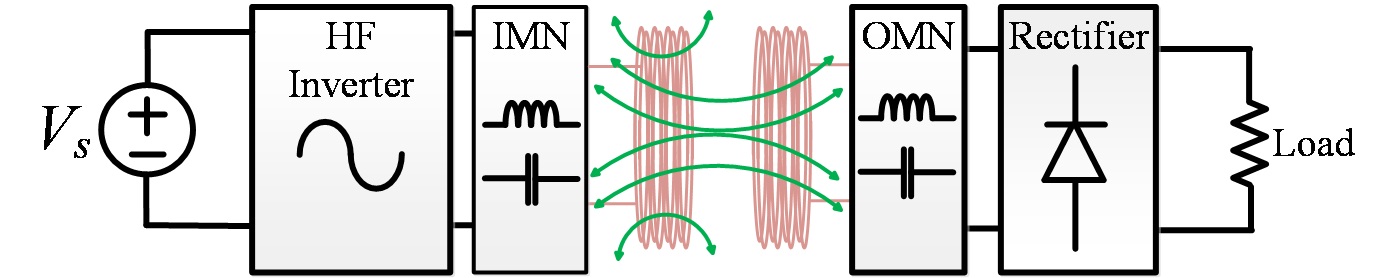
Inductive wireless power transfer |
The challenging of the WPT system can be listed as low efficiency, low output power quality, and health hazards.
At the Energy Conversion Circuit Laboratory (ECCL), we are focusing on the optimal design and new topology to improve the efficiency and output power quality of both inductive and capacitor wireless power transfer.
Source:
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DC-to-DC_converter
[2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wireless_power_transfer
[3] J. Dai and D. C. Ludois, "A Survey of Wireless Power Transfer and a Critical Comparison of Inductive and Capacitive Coupling for Small Gap Applications," in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 30, no. 11, pp. 6017-6029, Nov. 2015, doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2015.2415253.






